Monohybrid mice practice problems for monohybrid crosses answer key – Welcome to the captivating world of genetics, where monohybrid mice practice problems for monohybrid crosses unveil the secrets of inheritance and provide a gateway to unlocking the mysteries of life. This comprehensive guide offers a profound exploration of the fundamental principles of monohybrid crosses, empowering you with the knowledge and skills to delve into the fascinating realm of genetic inheritance.
Through a seamless blend of theoretical explanations, practical exercises, and insightful discussions, this resource equips you with a thorough understanding of monohybrid crosses, enabling you to confidently navigate the intricacies of genetic inheritance and unravel the complexities of genetic variation.
Monohybrid Crosses: A Guide to Understanding Mendelian Inheritance
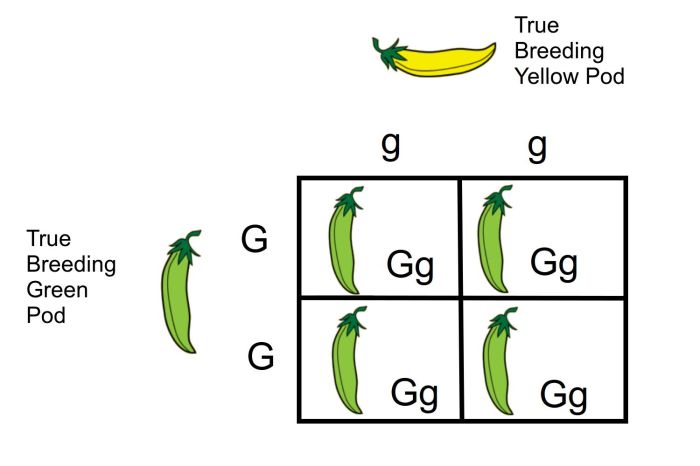
Monohybrid crosses are a fundamental concept in genetics that provide a simplified understanding of how traits are passed from parents to offspring. This guide will explain the basics of monohybrid crosses, including how to use Punnett squares, predict genotypes and phenotypes, and solve practice problems.
Punnett Square Analysis, Monohybrid mice practice problems for monohybrid crosses answer key
A Punnett square is a diagram used to predict the possible outcomes of a monohybrid cross. It consists of a grid with the alleles of one parent listed along the top and the alleles of the other parent listed along the side.
Each square in the grid represents a possible genotype of the offspring.
To use a Punnett square, follow these steps:
- Write the alleles of one parent along the top of the grid.
- Write the alleles of the other parent along the side of the grid.
- For each square in the grid, combine one allele from the top and one allele from the side.
The resulting grid will show all possible genotypes of the offspring. The probability of each genotype can be calculated by dividing the number of squares with that genotype by the total number of squares in the grid.
Genotype and Phenotype Predictions
The genotype of an organism is its genetic makeup, while the phenotype is its observable traits. In a monohybrid cross, the genotype of the offspring can be predicted by examining the Punnett square. The phenotype of the offspring can be predicted by knowing the dominant and recessive alleles for the trait being studied.
A dominant allele is an allele that is expressed in the phenotype even when only one copy of the allele is present. A recessive allele is an allele that is only expressed in the phenotype when two copies of the allele are present.
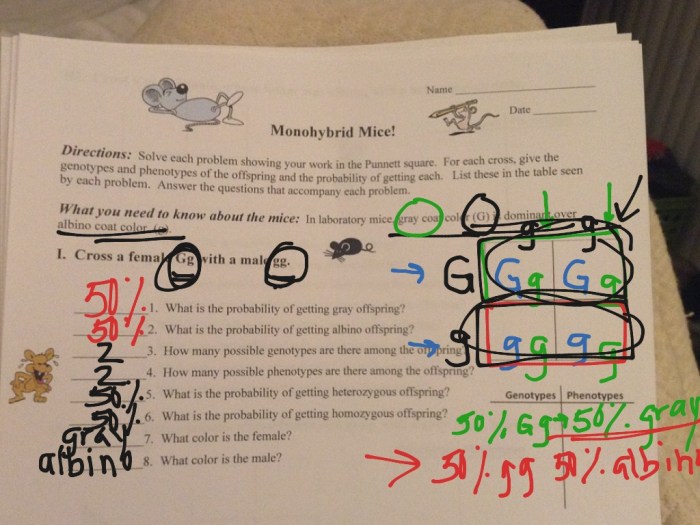
Practice Problems
To reinforce your understanding of monohybrid crosses, it is helpful to solve practice problems. Here are a few examples:
- A homozygous dominant pea plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive pea plant. What is the probability of obtaining a heterozygous offspring?
- A heterozygous snapdragon plant is crossed with a homozygous recessive snapdragon plant. What is the expected phenotypic ratio of the offspring?
An answer key for these practice problems is provided at the end of this guide.
Applications of Monohybrid Crosses
Monohybrid crosses are used in a variety of real-world applications, including plant and animal breeding. By understanding the principles of monohybrid crosses, scientists can predict the traits of offspring and select for desirable traits.
Monohybrid crosses have been used to improve agricultural yields and animal health. For example, monohybrid crosses have been used to develop disease-resistant crops and livestock.
User Queries: Monohybrid Mice Practice Problems For Monohybrid Crosses Answer Key
What is the purpose of monohybrid practice problems?
Monohybrid practice problems provide a structured approach to understanding the principles of monohybrid crosses and developing problem-solving skills in genetics.
How do I use a Punnett square to solve monohybrid crosses?
Arrange the parental genotypes along the top and side of the Punnett square, and fill in the squares with the possible offspring genotypes based on the laws of probability.
What is the difference between genotype and phenotype?
Genotype refers to the genetic makeup of an organism, while phenotype refers to the observable characteristics that result from the interaction between the genotype and the environment.