Label parts of microscope worksheet provides a comprehensive overview of the essential components of a microscope and their functions, empowering readers with a profound understanding of this indispensable scientific instrument. This guide delves into the intricacies of microscopy, unraveling the mechanisms behind magnification and illumination, and showcasing the diverse applications of this technology across various scientific disciplines.
Parts of a Microscope: Label Parts Of Microscope Worksheet
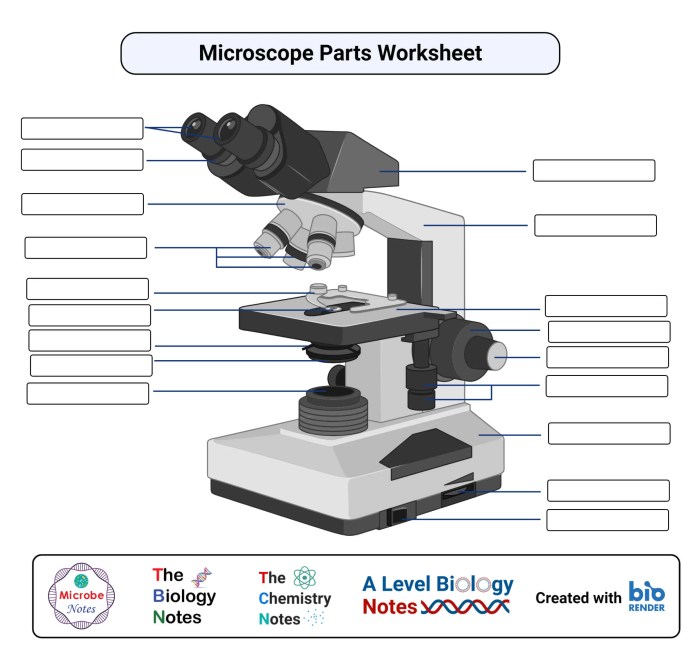
A compound microscope is a scientific instrument used to magnify small objects and observe their fine details. It consists of several major components that work together to produce a magnified image of the specimen being studied.
Eyepiece
The eyepiece, also known as the ocular lens, is the part of the microscope that the user looks through. It contains lenses that magnify the image produced by the objective lenses.
Objective Lenses, Label parts of microscope worksheet
Objective lenses are located at the bottom of the microscope and magnify the specimen. They come in different magnifications, allowing the user to choose the appropriate level of magnification for their observation.
Stage
The stage is the platform on which the specimen is placed. It can be moved up and down to focus the specimen and left and right to scan the specimen.
Condenser
The condenser is a lens that focuses light onto the specimen. It helps to illuminate the specimen and improve the contrast of the image.
Light Source
The light source provides illumination for the specimen. It can be a natural light source, such as sunlight, or an artificial light source, such as a lamp.
Functions of Microscope Parts
Each part of the microscope has a specific function that contributes to the overall magnification and illumination of the specimen.
Eyepiece
- Magnifies the image produced by the objective lenses.
- Provides a comfortable viewing position for the user.
Objective Lenses, Label parts of microscope worksheet
- Magnify the specimen by different amounts.
- Determine the total magnification of the microscope.
Stage
- Holds the specimen in place.
- Allows the user to move the specimen for observation.
Condenser
- Focuses light onto the specimen.
- Improves the contrast and resolution of the image.
Light Source
- Provides illumination for the specimen.
- Allows the user to adjust the intensity of the light.
Using a Microscope

Using a microscope requires proper techniques to ensure accurate and clear observation.
Focusing
- Start with the lowest magnification objective lens.
- Adjust the coarse focus knob to bring the specimen into rough focus.
- Switch to a higher magnification objective lens and use the fine focus knob for precise focusing.
Adjusting the Light
- Adjust the diaphragm to control the amount of light reaching the specimen.
- Use the condenser to focus the light onto the specimen.
Preparing Slides
- Place the specimen on a microscope slide.
- Add a drop of water or mounting medium to the specimen.
- Cover the specimen with a coverslip.
Applications of Microscopy
Microscopy has a wide range of applications in various fields, including:
Biology
- Study of cells, tissues, and microorganisms.
- Identification of bacteria and viruses.
Chemistry
- Analysis of crystal structures.
- Examination of chemical reactions.
Medicine
- Diagnosis of diseases.
- Examination of tissue samples.
Helpful Answers
What are the major components of a compound microscope?
The major components of a compound microscope include the eyepiece, objective lenses, stage, condenser, and light source.
How do objective lenses contribute to magnification?
Objective lenses magnify the image of the specimen, with higher magnification lenses providing a closer and more detailed view.
What is the function of the condenser in a microscope?
The condenser focuses light onto the specimen, providing optimal illumination for clear observation.