Delve into the fascinating world of geometry with our comprehensive Unit 6 Polygons and Quadrilaterals Answer Key. This invaluable resource provides a thorough understanding of the properties, types, and applications of these fundamental geometric shapes.
Our detailed guide explores the intricacies of polygons, including their number of sides, angles, and diagonals. We delve into the specific characteristics of quadrilaterals, examining their opposite sides and angles. Moreover, we present theorems and formulas essential for calculating the area, perimeter, and other measurements of these shapes.
Introduction to Polygons and Quadrilaterals
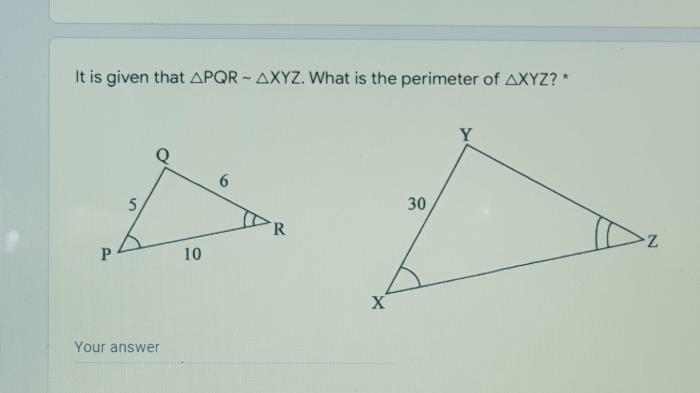
In geometry, a polygon is a closed figure formed by three or more line segments that intersect only at their endpoints. A quadrilateral is a polygon with four sides.
Polygons and quadrilaterals are fundamental shapes in geometry, with various properties and applications. Understanding their characteristics and relationships is essential for further exploration in geometry and related fields.
Types of Polygons
- Triangle: A polygon with three sides and three vertices.
- Quadrilateral: A polygon with four sides and four vertices.
- Pentagon: A polygon with five sides and five vertices.
- Hexagon: A polygon with six sides and six vertices.
- Heptagon: A polygon with seven sides and seven vertices.
- Octagon: A polygon with eight sides and eight vertices.
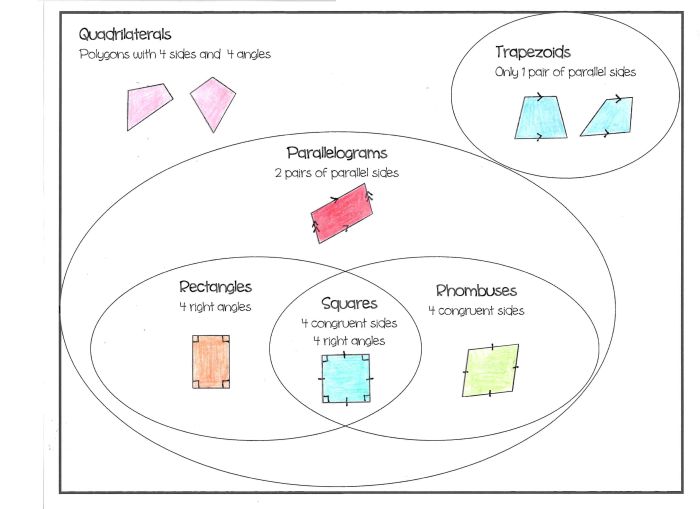
Types of Quadrilaterals
- Parallelogram: A quadrilateral with opposite sides parallel.
- Rectangle: A parallelogram with four right angles.
- Square: A rectangle with all four sides equal.
- Rhombus: A parallelogram with all four sides equal.
- Trapezoid: A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides.
Properties of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Properties of Polygons
- Number of sides: A polygon can have any number of sides, but it must have at least three sides to be considered a polygon.
- Number of angles: A polygon has the same number of angles as it has sides.
- Number of diagonals: The number of diagonals in a polygon with nsides is given by the formula n( n-3)/2.
Properties of Quadrilaterals
- Opposite sides: The opposite sides of a quadrilateral are parallel.
- Opposite angles: The opposite angles of a quadrilateral are equal.
- Diagonals: The diagonals of a quadrilateral bisect each other.
Theorems and Formulas for Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Theorems, Unit 6 polygons and quadrilaterals answer key
- Angle Sum Theorem: The sum of the interior angles of a polygon with nsides is ( n-2) – 180 degrees.
- Exterior Angle Theorem: The measure of an exterior angle of a polygon is equal to the sum of the measures of the two non-adjacent interior angles.
Formulas
- Area of a Triangle: A= (1/2) – b– h, where bis the length of the base and his the height.
- Area of a Rectangle: A= l– w, where lis the length and wis the width.
- Area of a Parallelogram: A= b– h, where bis the length of the base and his the height.
Applications of Polygons and Quadrilaterals
Polygons and quadrilaterals have numerous applications in real-world scenarios, including:
- Architecture: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of buildings, bridges, and other structures.
- Engineering: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the design of machines, vehicles, and other mechanical systems.
- Art and Design: Polygons and quadrilaterals are used in the creation of paintings, sculptures, and other works of art.
Quick FAQs: Unit 6 Polygons And Quadrilaterals Answer Key
What are the key characteristics of polygons?
Polygons are closed figures with straight sides and angles. They are classified based on the number of sides, with triangles having three sides, quadrilaterals having four sides, and so on.
How do you calculate the area of a quadrilateral?
The area of a quadrilateral can be calculated using various formulas depending on the type of quadrilateral. For example, the area of a rectangle is calculated by multiplying its length and width.
What are the different types of quadrilaterals?
Quadrilaterals are classified into various types based on their properties. Common types include squares, rectangles, parallelograms, trapezoids, and kites.