Articles of confederation vs constitution chart – The Articles of Confederation vs. Constitution chart unveils the stark contrasts between these two foundational documents, illuminating their distinct approaches to governance, power distribution, and representation. This in-depth comparison provides a comprehensive understanding of the evolution of the United States’ constitutional framework.
The Articles of Confederation, adopted in 1781, established a loose confederation of sovereign states, while the Constitution, ratified in 1789, created a stronger national government with expanded powers. These differences had profound implications for the functioning of the two systems, shaping the course of American history.
Structure and Governance: Articles Of Confederation Vs Constitution Chart
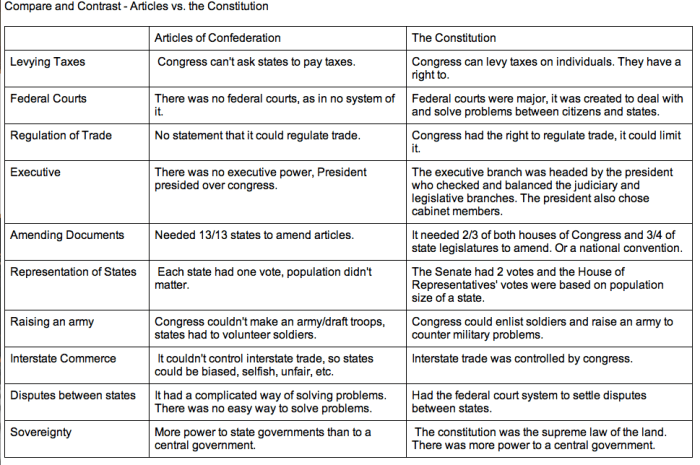
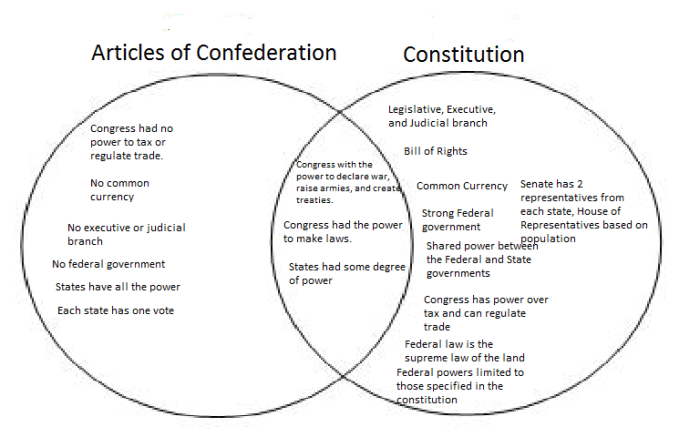
The Articles of Confederation established a loose confederation of sovereign states, while the Constitution created a more unified federal government. Under the Articles, each state had one vote in Congress, regardless of its population. This gave small states disproportionate power and made it difficult to pass legislation.
In contrast, the Constitution established a bicameral Congress with the House of Representatives based on population and the Senate with two senators from each state. This gave larger states more power but also ensured that the interests of smaller states were protected.
Powers of the Central Government
The Articles of Confederation granted the central government very limited powers. It could not tax, regulate commerce, or maintain an army or navy. As a result, the central government was weak and unable to effectively address national issues.
The Constitution, on the other hand, granted the central government significantly more powers. It gave Congress the power to tax, regulate commerce, declare war, and raise and maintain an army and navy. This made the central government much stronger and more capable of addressing national issues.
Representation and Suffrage, Articles of confederation vs constitution chart
Under the Articles of Confederation, each state had one vote in Congress, regardless of its population. This gave small states disproportionate power and made it difficult to pass legislation that benefited the larger states.
The Constitution established a bicameral Congress with the House of Representatives based on population and the Senate with two senators from each state. This gave larger states more power but also ensured that the interests of smaller states were protected.
In addition, the Constitution expanded suffrage to all white male citizens over the age of 21. This was a significant change from the Articles of Confederation, which limited suffrage to property owners.
Amendments and Ratification
The Articles of Confederation required unanimous consent from all 13 states to amend. This made it extremely difficult to make changes to the Articles, even when they were necessary.
The Constitution, on the other hand, established a more flexible amendment process. Amendments can be proposed by two-thirds of Congress or by a national convention called by Congress at the request of two-thirds of the states. Amendments are then ratified by three-fourths of the states.
Historical Context
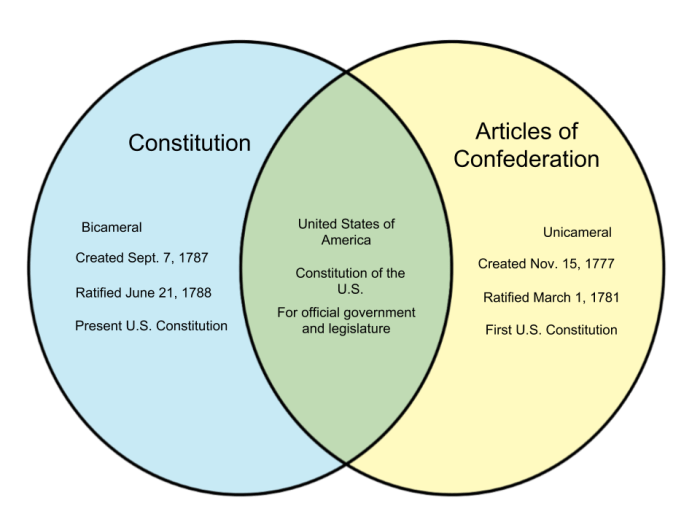
The Articles of Confederation were drafted in 1777, shortly after the American Revolution. At the time, the United States was a young nation with a weak central government. The Articles were designed to create a loose confederation of states that would allow each state to retain its sovereignty.
However, the Articles proved to be inadequate to meet the needs of the growing nation. The central government was too weak to address national issues, such as regulating commerce and maintaining an army and navy. As a result, the Constitution was drafted in 1787 to replace the Articles.
Question Bank
What were the key differences between the Articles of Confederation and the Constitution?
The Articles established a loose confederation of states with limited central authority, while the Constitution created a stronger national government with expanded powers.
How did the Articles of Confederation impact the functioning of the government?
The Articles’ weak central government and lack of enforcement mechanisms made it difficult to address national issues and maintain order.
Why was the Constitution drafted?
The Articles of Confederation proved inadequate for the challenges of a growing nation, leading to the drafting of the Constitution, which provided a more effective framework for governance.