The microbiology department in the laboratory performs a crucial role in healthcare, research, and industry. Its primary functions encompass diagnostic testing, microbial identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and infection control. This department plays a vital role in safeguarding public health and advancing scientific knowledge.
Microbiology laboratories utilize advanced techniques such as microscopy, culturing, staining, and molecular diagnostics to identify and characterize microorganisms. Quality control and regulatory compliance are paramount to ensure accurate and reliable results. Microbiology professionals, including microbiologists, laboratory technicians, and support staff, undergo rigorous training to maintain high standards of practice.
Introduction
Microbiology departments in laboratories play a crucial role in various fields, including healthcare, research, and industry. They provide essential services related to the diagnosis, prevention, and treatment of infectious diseases.
In healthcare settings, microbiology departments perform diagnostic testing to identify and characterize microorganisms causing infections. They also conduct antimicrobial susceptibility testing to guide appropriate antibiotic therapy. Furthermore, microbiology departments contribute to infection control by monitoring and preventing the spread of infectious agents within healthcare facilities.
In research institutions, microbiology departments are involved in studying the biology, pathogenesis, and epidemiology of microorganisms. They conduct basic and applied research to develop new diagnostic methods, vaccines, and treatments for infectious diseases.
In industry, microbiology departments provide quality control services for food, water, and pharmaceutical products. They ensure the safety and quality of these products by testing for the presence of pathogenic microorganisms and monitoring compliance with regulatory standards.
Functions of a Microbiology Department
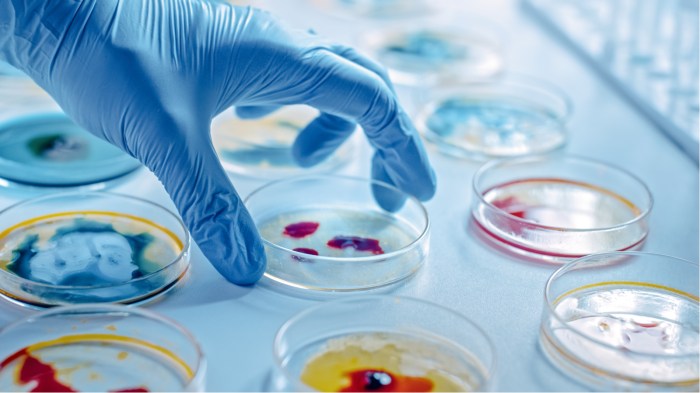
Diagnostic Testing
Microbiology departments perform diagnostic testing to identify and characterize microorganisms causing infections. This involves collecting samples from patients, such as blood, urine, or tissue biopsies, and subjecting them to various laboratory tests.
Common diagnostic techniques include microscopy, culturing, and molecular diagnostics. Microscopy allows for the visualization of microorganisms, while culturing enables the isolation and identification of specific bacteria or fungi. Molecular diagnostics, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction), provide rapid and sensitive detection of specific pathogens.
Microbial Identification
Microbiology departments play a vital role in microbial identification, which is essential for accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment of infections. They use a variety of techniques to identify microorganisms, including:
- Morphological and biochemical characteristics
- Serological testing
- Molecular diagnostics
Accurate microbial identification helps clinicians determine the most effective treatment options and implement appropriate infection control measures.
Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing is a crucial function of microbiology departments. It determines the effectiveness of different antibiotics against specific microorganisms, guiding appropriate antibiotic therapy.
Microbiology departments use standardized methods, such as the Kirby-Bauer disk diffusion test or broth microdilution, to measure the susceptibility of microorganisms to various antibiotics. The results of these tests help clinicians select the most appropriate antibiotics for treating infections.
Infection Control
Microbiology departments play a significant role in infection control by monitoring and preventing the spread of infectious agents within healthcare facilities. They conduct environmental sampling, surveillance, and outbreak investigations to identify potential sources of infection and implement appropriate control measures.
Microbiology departments also provide guidance on infection prevention practices, such as hand hygiene, isolation precautions, and the use of personal protective equipment. By implementing these measures, they help prevent the transmission of infectious diseases and protect patients and healthcare workers.
Microbiology Laboratory Techniques
Microscopy
Microscopy is a fundamental technique in microbiology, allowing for the visualization and examination of microorganisms. Microbiology departments use different types of microscopes, including bright-field, dark-field, and fluorescence microscopes.
Microscopy enables microbiologists to observe the morphology, size, and arrangement of microorganisms, as well as their motility and staining characteristics. This information is crucial for microbial identification and understanding their behavior.
Culturing
Culturing is a technique used to isolate and grow microorganisms in a controlled environment. Microbiology departments use various culture media, such as agar plates or broth cultures, to provide specific nutrients and conditions for microbial growth.
Culturing allows microbiologists to obtain pure cultures of specific microorganisms, which can then be used for further characterization, identification, and antimicrobial susceptibility testing.
Staining
Staining is a technique used to enhance the visibility and differentiation of microorganisms under a microscope. Microbiology departments use different staining methods, such as Gram staining and acid-fast staining, to highlight specific characteristics of microorganisms.
Staining techniques enable microbiologists to differentiate between different types of bacteria, such as Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, and to identify specific microorganisms based on their staining properties.
Molecular Diagnostics, The microbiology department in the laboratory performs
Molecular diagnostics are rapidly evolving techniques used to identify and characterize microorganisms at the molecular level. Microbiology departments utilize molecular diagnostics, such as PCR (polymerase chain reaction) and DNA sequencing, to detect specific genetic sequences associated with microorganisms.
Molecular diagnostics provide rapid and sensitive detection of pathogens, enabling early diagnosis and appropriate treatment. They also play a role in microbial epidemiology and outbreak investigations.
Quality Control and Regulations

Quality control is paramount in microbiology laboratories to ensure the accuracy and reliability of diagnostic testing. Microbiology departments implement strict quality control measures, including:
- Regular calibration and maintenance of laboratory equipment
- Use of standardized operating procedures
- Participation in external proficiency testing programs
Microbiology departments also adhere to regulatory standards, such as those established by the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA) in the United States and ISO 15189 internationally. These regulations ensure that microbiology laboratories meet specific quality and performance requirements.
Staff and Training

Microbiologists
Microbiologists are scientists with specialized training in microbiology. They are responsible for performing diagnostic testing, microbial identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and infection control measures.
Microbiologists typically hold a master’s degree or doctorate in microbiology or a related field.
Laboratory Technicians
Laboratory technicians are individuals with technical training in laboratory procedures. They assist microbiologists with diagnostic testing, sample preparation, and other laboratory tasks.
Laboratory technicians typically hold an associate’s degree or certificate in laboratory science or a related field.
Support Staff
Support staff, such as administrative assistants and laboratory aides, provide essential support to microbiology departments. They handle administrative tasks, maintain laboratory equipment, and assist with sample collection and processing.
Emerging Trends in Microbiology

Advanced Molecular Diagnostics
Advanced molecular diagnostics, such as next-generation sequencing (NGS) and multiplex PCR, are revolutionizing microbiology. These techniques provide rapid and comprehensive identification of microorganisms, including those that are difficult to culture or identify using traditional methods.
Advanced molecular diagnostics have applications in outbreak investigations, antimicrobial resistance surveillance, and personalized medicine.
Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine in microbiology involves tailoring treatment strategies to individual patients based on their genetic makeup and microbial profile. This approach aims to optimize antibiotic therapy and prevent the development of antimicrobial resistance.
Microbiology departments are actively involved in research and development of personalized medicine approaches, such as using molecular diagnostics to identify patients at risk for specific infections or to guide antibiotic selection.
Automation and Artificial Intelligence
Automation and artificial intelligence (AI) are increasingly being used in microbiology laboratories. Automated systems can perform repetitive tasks, such as sample preparation and data analysis, freeing up microbiologists to focus on more complex tasks.
AI algorithms can assist in microbial identification, antimicrobial susceptibility testing, and outbreak detection. These technologies have the potential to improve efficiency, accuracy, and turnaround time in microbiology laboratories.
Answers to Common Questions: The Microbiology Department In The Laboratory Performs
What is the primary role of a microbiology department in a laboratory?
The primary role of a microbiology department is to identify and characterize microorganisms, perform diagnostic testing, determine antimicrobial susceptibility, and implement infection control measures.
What are the essential laboratory techniques used in microbiology?
Essential laboratory techniques include microscopy, culturing, staining, and molecular diagnostics.
Why is quality control important in microbiology laboratories?
Quality control is crucial to ensure accurate and reliable results, which are essential for patient care and scientific research.