The metering device in the refrigeration cycle converts high-pressure liquid refrigerant to a low-pressure vapor, playing a crucial role in regulating refrigerant flow and maintaining optimal conditions for efficient operation. This intricate process involves a delicate balance of pressure and temperature regulation, ensuring the smooth functioning of refrigeration systems.
Metering devices come in various types, each with its advantages and disadvantages. Understanding their functionality and design considerations is essential for optimizing refrigeration system performance and troubleshooting common issues. By delving into the intricacies of metering devices, we gain valuable insights into the heart of refrigeration technology.
Metering Device Functionality
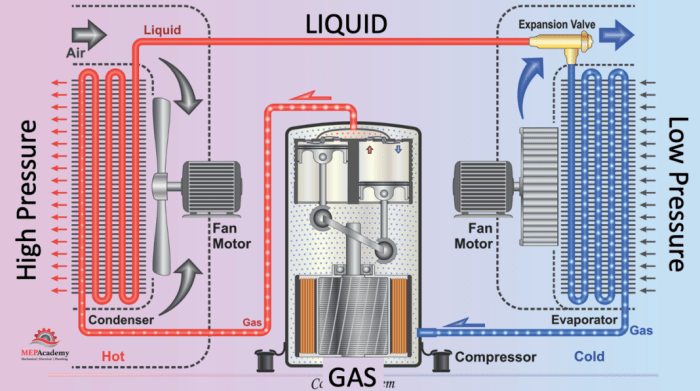
The metering device is a crucial component in the refrigeration cycle, responsible for controlling the flow of refrigerant. It acts as an expansion valve, converting high-pressure liquid refrigerant into a low-pressure vapor.
The metering device ensures the precise delivery of refrigerant to the evaporator, maintaining the optimal refrigerant charge and preventing system inefficiencies.
Types of Metering Devices, The metering device in the refrigeration cycle converts
- Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TXV):Self-regulating valve that adjusts refrigerant flow based on the evaporator temperature.
- Capillary Tube:A long, narrow tube with a fixed orifice, providing constant refrigerant flow.
- Electronic Expansion Valve (EEV):Computer-controlled valve that modulates refrigerant flow based on various parameters.
Conversion Process
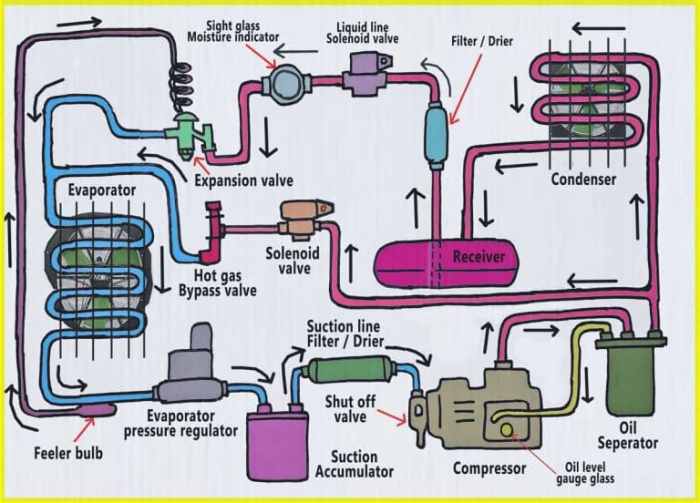
The metering device converts high-pressure liquid refrigerant to a low-pressure vapor through a process known as throttling.
As the liquid refrigerant passes through the narrow orifice of the metering device, it undergoes a rapid pressure drop. This sudden pressure reduction causes the refrigerant to vaporize, resulting in a mixture of liquid and vapor.
Pressure and Temperature Regulation
The metering device plays a critical role in regulating pressure and temperature within the refrigeration cycle.
By controlling the refrigerant flow, the metering device maintains the desired evaporator pressure, ensuring efficient heat transfer and refrigerant evaporation. It also helps prevent excessive pressure in the condenser, minimizing energy consumption and system wear.
Design Considerations
The design of metering devices involves several considerations:
- Size and Shape:Influenced by the refrigerant flow rate and pressure drop requirements.
- Materials:Must be compatible with the refrigerant and withstand the operating conditions.
- Response Time:Determines the ability of the device to adjust refrigerant flow in response to changing conditions.
Troubleshooting and Maintenance
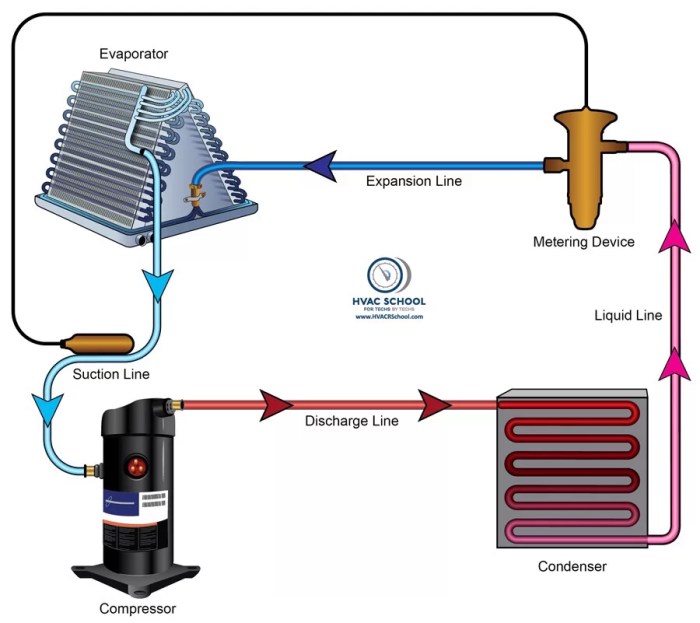
Common issues associated with metering devices include:
- Overfeeding:Excess refrigerant flow, leading to reduced cooling capacity and increased energy consumption.
- Underfeeding:Insufficient refrigerant flow, resulting in poor heat transfer and system inefficiency.
- Clogged or Dirty Orifice:Restricts refrigerant flow, affecting system performance.
Regular maintenance, such as cleaning and inspection, helps prevent these issues and ensures optimal metering device performance.
FAQ Compilation: The Metering Device In The Refrigeration Cycle Converts
What is the primary function of a metering device in a refrigeration cycle?
The primary function of a metering device is to control the flow of refrigerant by converting high-pressure liquid refrigerant to a low-pressure vapor, maintaining the desired pressure and temperature conditions for efficient refrigeration.
What are the different types of metering devices used in refrigeration systems?
Common types of metering devices include capillary tubes, thermostatic expansion valves, and electronic expansion valves, each with its unique characteristics and applications.
How does the metering device regulate pressure and temperature in the refrigeration cycle?
The metering device maintains pressure and temperature by controlling the flow of refrigerant, ensuring that the evaporator receives the optimal amount of refrigerant for efficient heat absorption and that the compressor receives refrigerant vapor at the appropriate pressure.