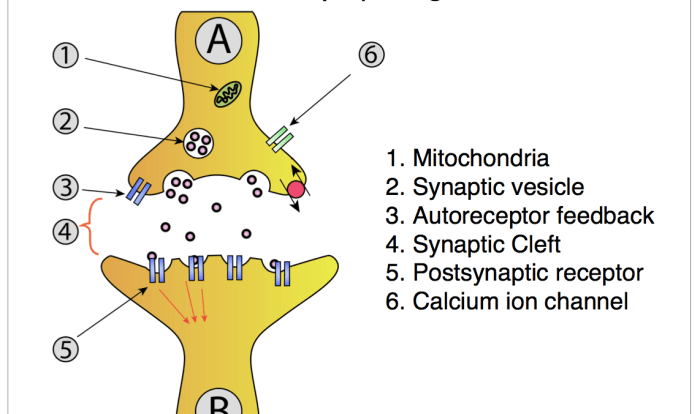
Which of the following statements accurately defines neuroglial cells? Neuroglial cells, often referred to as glial cells, are non-neuronal cells that constitute the majority of the central nervous system. They play a critical role in maintaining homeostasis, providing structural support, and facilitating neuronal communication.
Neuroglial cells are essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system, and their dysfunction can lead to various neurological disorders. Understanding their diverse functions and characteristics is crucial for comprehending the intricate workings of the brain and spinal cord.
Definition of Neuroglial Cells

Neuroglial cells, also known as glial cells, are specialized cells found within the nervous system. They outnumber neurons by a ratio of 10:1 and play crucial roles in supporting and maintaining the healthy functioning of neurons.
Unlike neurons, neuroglial cells do not transmit electrical signals. Instead, they provide structural support, insulation, and metabolic nourishment to neurons, ensuring their optimal performance and survival.
Functions of Neuroglial Cells

Neuroglial cells perform a wide range of functions essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. These functions include:
- Structural support:Neuroglial cells provide physical support to neurons, helping to maintain the architecture of the nervous system and protect neurons from mechanical damage.
- Insulation:Myelinating neuroglial cells, such as oligodendrocytes in the central nervous system and Schwann cells in the peripheral nervous system, wrap around axons, forming an insulating layer called myelin. Myelin allows for faster and more efficient transmission of electrical signals along neurons.
- Metabolic nourishment:Neuroglial cells supply nutrients and oxygen to neurons, ensuring their metabolic needs are met.
- Waste removal:Neuroglial cells help remove waste products from the nervous system, maintaining a clean and healthy environment for neurons to function.
- Immune defense:Neuroglial cells play a role in the immune defense of the nervous system, helping to protect against infections and other harmful substances.
Types of Neuroglial Cells: Which Of The Following Statements Accurately Defines Neuroglial Cell

There are several types of neuroglial cells, each with its own specific location and function. The major types of neuroglial cells include:
| Type | Location | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Astrocytes | Central nervous system | – Provide structural support
|
| Oligodendrocytes | Central nervous system | – Form myelin sheaths around axons |
| Schwann cells | Peripheral nervous system | – Form myelin sheaths around axons |
| Microglia | Central nervous system | – Immune defense
|
| Ependymal cells | Central nervous system | – Line the ventricles and central canal
|
Importance of Neuroglial Cells
Neuroglial cells are essential for the healthy functioning of the nervous system. Their roles in providing structural support, insulation, metabolic nourishment, waste removal, and immune defense are crucial for the proper functioning of neurons and the overall health of the nervous system.
Dysfunction of neuroglial cells can lead to a variety of neurological disorders, such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease. Therefore, understanding the role of neuroglial cells is critical for developing effective treatments for these and other neurological conditions.
Research and Applications
Current research on neuroglial cells focuses on understanding their role in various neurological disorders and developing therapies that target neuroglial cells to treat these disorders.
For example, research has shown that dysfunction of astrocytes is implicated in the development of Alzheimer’s disease. By understanding the role of astrocytes in this disease, researchers hope to develop therapies that target astrocytes to slow or prevent the progression of Alzheimer’s disease.
FAQ Explained
What are the main types of neuroglial cells?
There are several types of neuroglial cells, including astrocytes, oligodendrocytes, microglia, and Schwann cells, each with distinct functions and locations within the nervous system.
How do neuroglial cells contribute to neuronal communication?
Neuroglial cells play a crucial role in facilitating neuronal communication by insulating axons, removing neurotransmitters from the synaptic cleft, and providing metabolic support to neurons.
What are the consequences of neuroglial cell dysfunction?
Dysfunction of neuroglial cells can lead to a range of neurological disorders, including multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, as they disrupt the delicate balance of the nervous system.